TICK-BORNE DISEASE TEST METHODOLOGIES
IGeneX offers a broad range of serological and molecular tests for Tick-Borne diseases. The serological tests include ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay), IFA (Indirect Immunofluorescent Assay), Western Blots, ImmunoBlots, IgXSpot, and LDA (Lyme Dot-Blot Assay). The molecular tests include PCR and FISH (Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization).
IMMUNOBLOTS
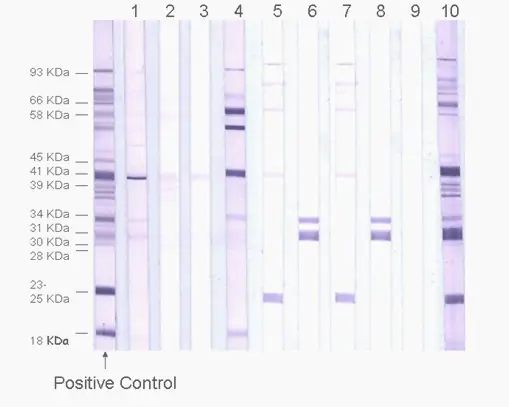
The IgM and IgG ImmunoBlot (IB) are qualitative immunoassays in which antibodies are visualized. They are used to determine whether pathogen-specific antibodies are present in patient serum or plasma. These tests are generally more sensitive and specific than the Western Blot, ELISA, and IFA tests.
How it Works
Step 1: IB strip preparation: IB strips are prepared from recombinant proteins of interest. The recombinant proteins are applied to a membrane and cut into strips.
Step 2: Patient serum or plasma is incubated with the IB strip. If specific antibodies to pathogen antigens are present, they will bind to the corresponding antigen bands.
Step 3: After washing off the unbound serum, the strip is incubated with alkaline phosphate-conjugated goat anti-human antibody. Bound antibodies react with BCIP/NBT, a chromogenic substrate. A dark purple colored precipitate develops on the antigen-antibody complexes. Bands are visualized and scored for intensities relative to the positive and negative controls. (See right)
ImmunoBlot strip example
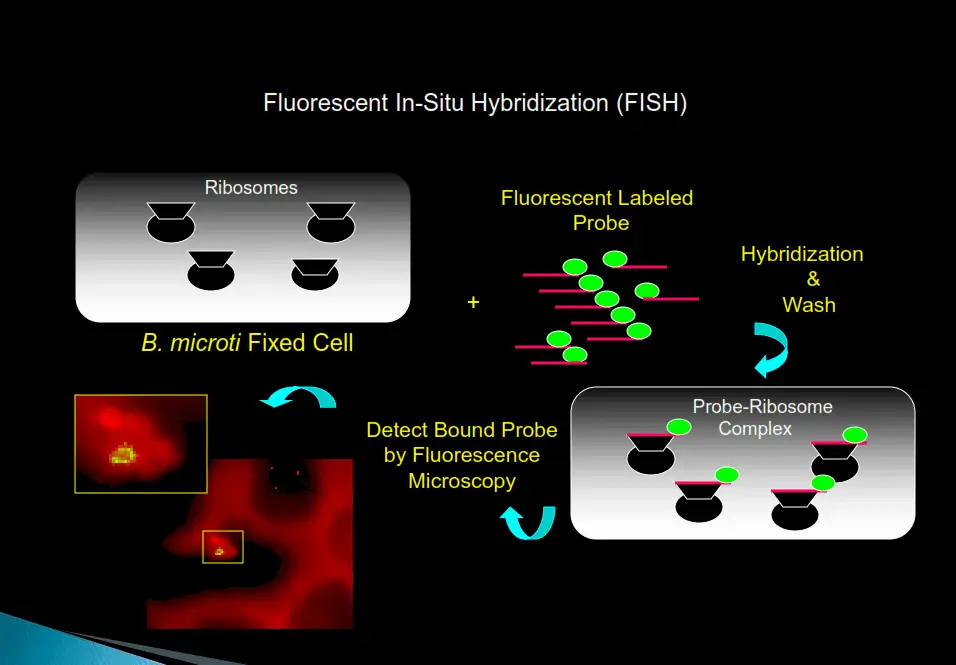
FISH (FLUORESCENT IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION)
The FISH test provides a significant increase in sensitivity and specificity over standard Giemsa-stained smears for the presence of bacteria, fungi, and intraerythrocytic parasites (piroplasts) in red blood cells.
How it Works
Step 1: A methanol-fixed blood smear is created from a patient’s blood sample.
Step 2: After adding the hybridization buffer with a pathogen-specific probe labeled with a fluorescent dye, the slide is incubated for a short time at 37℃. The pathogen rRNA will hybridize with the pathogen if present in the blood smear.
Step 3: After hybridization is complete, the excess probe is removed by washing with a special wash solution.
Step 4: The smear is dried, and counter-stain is added. The slide is then viewed with a fluorescent microscope; if pathogens are present, the blood smear will fluoresce.
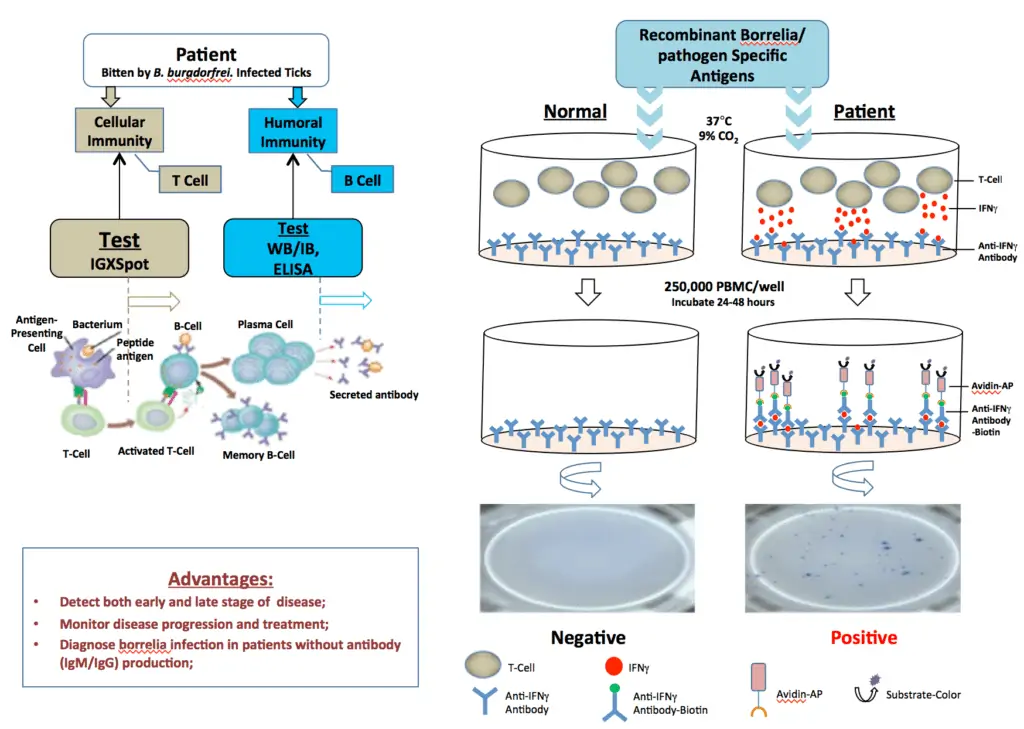
IGXSPOT
The IgXSpot is an enzyme-linked immunospot assay that detects human T cells reactive to borrelia/pathogen-specific antigens in vitro. It is well documented that both humoral and cellular immune responses develop in borrelia/pathogen infection. The cellular immune response develops much earlier than the humoral response in most patients who are infected with borrelia species. In some patients, sero-conversion from cellular to humoral response does not occur or occurs much later in the disease. In some patients with a chronic form of the disease, the humoral response is poor. Therefore, the IgXSpot test is recommended for detection of very early and/or late borrelia/pathogen infection and in seronegative patient’s whole blood samples.
Principle
ELISPOT is a widely used method for detecting and monitoring cellular immune responses to specific antigens. The IgXSpot assay allows visualization of the secretory product(s) of individual activated or responding cells to borrelia-specific antigens. Each spot that develops in the assay represents a single reactive cell.
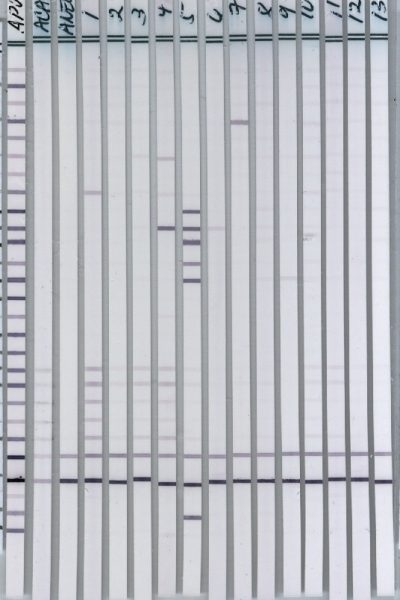
WESTERN BLOTS
The IgG and IgM Western Blots are qualitative immunoassays in which antibodies are visualized. They are used to determine whether pathogen-specific antibodies are present in patient serum or plasma. These tests are generally more sensitive and specific than the ELISA and IFA tests.
How it Works
Step 1: Western Blot strips are prepared from a cell lysate of the pathogen of interest. Briefly, pathogen cell lysate is fractionated on acrylamide gel by electrophoresis.
Step 2: The separated proteins are then transferred from the gel to membranes, which are washed, dried, and sliced into 5 mm strips.
Step 3: Patient serum or plasma is incubated with a Western Blot strip. If specific antibodies to pathogen antigens are present, they will bind to the corresponding antigen bands.
Step 4: After washing off the unbound serum, each strip is incubated with alkaline phosphate-conjugated goat anti-human antibody. Bound antibodies react with BCIP/NBT, a chromogenic substrate. A dark purple colored precipitate develops on the antigen-antibody complexes. Bands are then visualized and scored for intensities relative to the positive and negative controls.
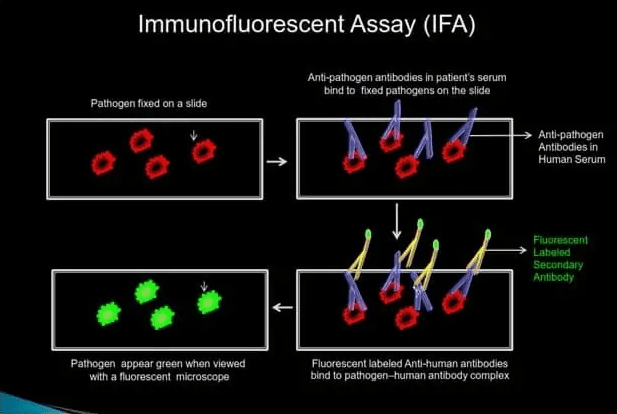
IFA (INDIRECT IMMUNOFLUORESCENT ASSAY)
IFA indirectly detects pathogen-specific IgG or IgM antibodies in patient serum.
How it Works
Step 1: Patient serum is added onto the slide with fixed pathogens. If pathogen-specific IgG or IgM antibodies are present in the human serum, they will bind to the fixed pathogen on the slide.
Step 2: Unbound serum is removed by washing the slide with a wash buffer, and a fluorescent-labeled anti-human antibody is added.
Step 3: After washing off the excess secondary antibody, the slide is viewed under a fluorescent microscope. If pathogen-specific antibodies are present in the human serum, fixed pathogen on the slide will fluoresce bright green when viewed with a fluorescent microscope.
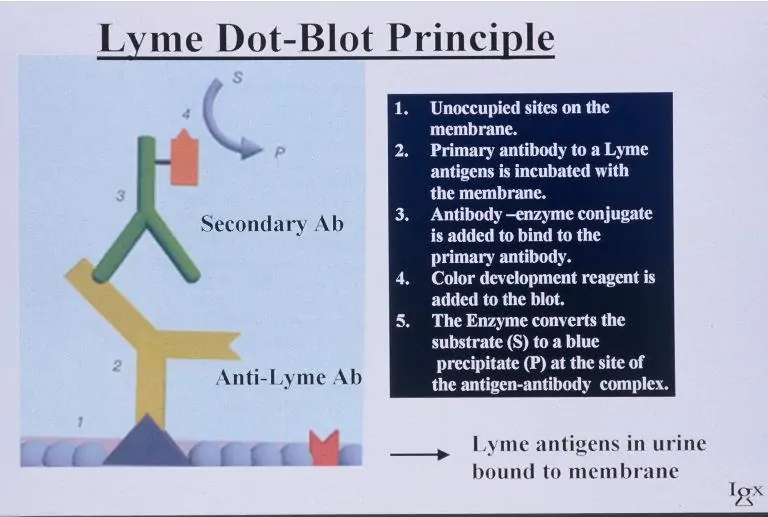
LDA (LYME DOT-BLOT ASSAY)
Lyme Dot-Blot Assay (LDA) is a qualitative immunoassay for the direct detection of Borrelia burgdorferi-specific antigens in a patient urine sample using anti-B. burgdorferi antibodies.
If the initial Lyme panel tests on a patient’s blood samples are negative, including PCR, but symptoms for Lyme disease are present, the Lyme Dot-blot assay on urine can be helpful in making the diagnosis.
How it Works
Step 1: The antigens present in the urine sample are immobilized onto a membrane in a Dot-blot format and incubated with anti-B. burgdorferi-specific antibodies.
Step 2: After washing the bound anti-B. burgdorferi-specific antibodies, they are reacted with anti-rabbit IgG, which is visualized by an enzyme/substrate reaction.
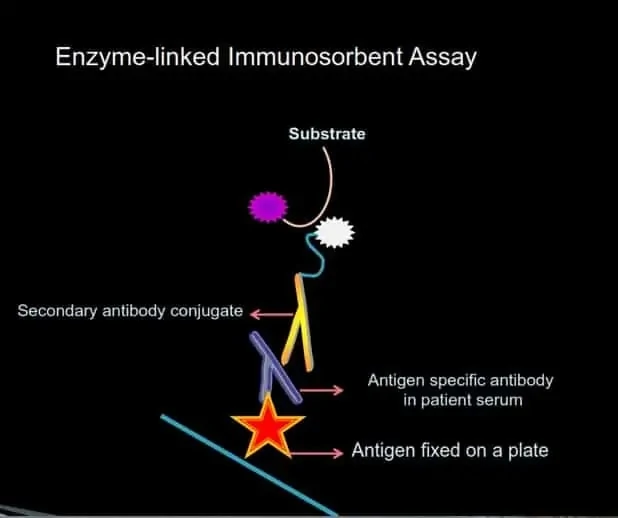
ELISA (ENZYME-LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY)
ELISA is a plate-based assay technique designed for detecting and quantifying pathogen-specific antibodies.
How it Works
Step 1: Cell lysate or antigens (including peptides) are immobilized to a solid surface and then complexed with a patient’s anti-pathogen antibody (primary antibody).
Step 2: The pathogen-bound human antibody is captured by an anti-human antibody linked to an enzyme (secondary antibody).
Step 3: Detection is accomplished by assessing the conjugated enzyme activity via incubation with a substrate to produce a measurable product.
- Enables accurate identification of biochemically unusual strains of pathogen
- Facilitates much earlier detection of the microorganism because the assay is independent of the host’s immune response schedule
- Allows monitoring of the efficacy of an antibiotic regime
- Can be performed on any type of sample: EDTA whole blood, serum, cerebral spinal fluid, synovial fluid, urine, breast milk, tissue biopsy and ticks.
- The combination of these factors imparts very high specificity and sensitivity to the test.
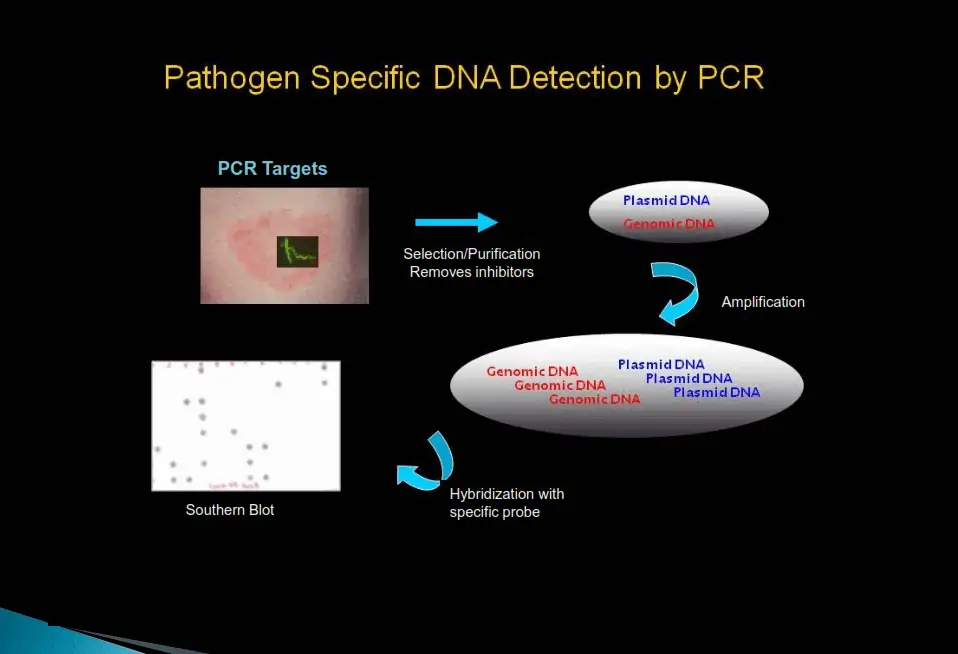
PCR
IGeneX offers traditional and real-time PCR Lyme tests and PCR tests for co-infections. The tests were developed in-house from clinical samples using our proprietary hybrid-select method.
The standard PCR test is not always sensitive enough when very few organisms are present in a sample. Furthermore, PCR sensitivity is well known to reduce in the presence of inhibitors. Therefore, IGeneX has developed nucleic-acid-based PCR diagnostic assays that are highly sensitive and specific. Theoretically, these PCR tests can be performed on any type of sample. They offer enhanced performance compared to microbiological, immunological, and amplified tests that are currently available for the detection of microorganisms in test samples.
How it Works
Step 1: Selection hybridization
Specifically removes the “common PCR inhibitors” from the clinical sample while simultaneously selecting and purifying the DNA fragment of interest. This procedure also concentrates the fragment of interest, thereby improving sensitivity.
Step 2: PCR amplification
The purified pathogen DNA fragment of interest is PCR-amplified with pathogen-specific primers. This sequence “hybridizes” or binds specifically to pathogen DNA of interest under predetermined PCR conditions. Therefore, only pathogen-specific DNA is amplified.
Step 3: Detection of amplified products
The PCR-amplified products are transferred and bound to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane-bound, PCR-amplified products are hybridized with pathogen-specific probes. Only samples with pathogen-specific DNA hybridize to the probes and give a blue-purple color dot on the membrane.
WHY IGENEX FOR TICK-BORNE DISEASE TESTING?

- CLIA certified in all 50 states
- Long track record of success since 1991
- Offers testing that is nearly twice as accurate as CDC recommended tests
- Tests for all major tick-borne illnesses, including Lyme disease, TBRF, Babesia, Bartonella, and Rickettsia
- Utilizes comprehensive testing methods such as PCR, ImmunoBlots, IgXSpot and FISH
- Has become a nationwide leader in COVID-19 testing due to a relentless focus on customer satisfaction
