Diagnostic Tests for Babesia
A Babesia diagnosis should be considered in patients who live in or travel to endemic areas for Babesiosis and experience a viral-like illness, have been bitten by Ixodes ticks, or have recently had a blood transfusion.
As the symptoms and signs of Babesiosis are relatively nonspecific, laboratory testing is required for a Babesia diagnosis. IGeneX offers the diagnostic tests listed below to help physicians accurately detect Babesia. Learn how each test works with the following guides and determine which test is right for you.
WHAT TESTS ARE AVAILABLE FOR BABESIOSIS?
IGeneX offers ImmunoBlots, IFAs (Indirect Immunofluorescent Assay), PCRs (Polymerase Chain Reaction), Culture Enhanced PCR (cePCR), and FISH (Fluorescent In-Situ Hybridization) tests to confirm the diagnosis of Babesia.
Babesia ImmunoBlots IgM and IgG
Babesia is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. However, unlike other tick-borne diseases, it is caused by microscopic parasites that infect red blood cells. This makes it similar to malaria. Babesia is the most common Lyme disease co-infection, and therefore testing is recommended if testing your patients for Lyme. The IGeneX Babesia ImmunoBlot tests for the Babesia genus and speciates to multiple species of Babesia that infect humans, including B. microti and B. duncani.
Principle
ImmunoBlotting is a form of IgM and IgG testing that uses multiple pure, recombinant proteins sprayed in precise amounts at specific positions on the test strips to dramatically increase accuracy. It has long been considered the gold standard in infectious disease testing for superior sensitivity and specificity. These tests effectively replace traditional tests such as ELISA and the western blot.
Until recently, diagnostic tests for Babesia have been grossly imprecise and have not been able to detect many of the ever-growing lists of species and strains. The IGeneX ImmunoBlots testing overcomes these obstacles with the ability to detect antibodies to multiple species of Babesia, including B. microti and B. duncani.
Advantages
- Uses specifically created recombinant proteins and not proteins from cultures
- Unlike IFA, can detect multiple species in one test
- Detects the full spectrum of disease: early, active and late-stage
- Detects Babesia genus and speciates to B. microti and B. duncani
- Avoids the error prone process of visualizing slides through a microscope
Included Antigens
B. microti and B. duncani
SAMPLE REQUIREMENT: 1.0 ml serum
TEST NUMBER: 900* Babesia IgM ImmunoBlot 905* Babesia IgG ImmunoBlot
CPT CODE: 87299, 86753, 86318, 87451 – 86753 x2, 86318, 87451
STAGE OF DISEASE: Any
Download datasheet >
View webinar >
View Babesia ImmunoBlot tests >
Babesia IFA
The Babesia Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA) is designed to detect human IgM and IgG antibodies to Babesia antigens in human serum. For diagnostic purposes, Babesia IFA test results should be used in conjunction with other information available to the diagnosing physician. Currently, IGeneX offers both B. microti and B. duncani IFA tests.
Principle
The Babesia IFA is a two-stage sandwich assay, which is based on an antigen-antibody-complex formation involving the following steps:
- Binding of anti-Babesia specific antibodies in human serum to fixed Babesia on a slide.
- Binding of fluorescent-labeled anti-human IgG/IgM antibodies specific to the human anti-Babesia antibodies bound to fixed Babesia on the slide.
- Identifying green fluorescing Babesia parasites with a fluorescent microscope.
Reference Range
Babesia antibody titers IgM <20
Babesia antibody titers IgG <40
Clinical Significance
The Babesia IFA antibody test detects antibodies targeting Babesia in human serum. Babesia titers rise during the first two to four weeks of illness and then decline over the next six-to-12 months. An IgG titer of less than 160 may indicate a resolving infection in patients with previously high titers. If the IFA is negative but clinical symptoms are present, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and/or fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) testing are suggested. Babesia is carried by the same species of ticks that cause Ehrlichiosis, Bartonellosis, and Lyme disease. Therefore, patients with positive titers should also be tested for other tick-borne diseases.
Stage of Disease
Any Stage of Disease (Early to Late/Chronic Stage)
Limitations
- A single negative IFA test result does not exclude the possibility of Babesia
- Other Babesia antibodies may cross-react and yield a false positive Babesia IFA test.
- Results should be interpreted in conjunction with other laboratory and clinical findings.
Babesia IFA Results Interpretation >
View Babesia IFA tests >
Babesia FISH
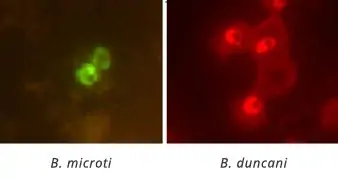
The Babesia Fluorescent In-Situ Hybridization (FISH) assay is designed for the qualitative detection of ribosomal RNA of Babesia parasites directly in a blood smear. The test’s high degree of specificity is provided by nucleic acid probes, which bind to RNA sequences of the Babesia. This test detects Babesia.
Principle
The FISH assay is based on two fundamental principles:
- Hybridization directly on a thin blood smear with a fluorescein-labeled Babesia specific probe
- Identification of Babesia parasites within the red blood cell by viewing with a fluorescent microscope
Reference Range
Babesia: Negative, Babesia specific rRNA not detected.
Clinical Significance
The FISH assay provides a significant increase in sensitivity and specificity over standard Giemsa-stained smears for the presence of intraerythrocytic parasites (piroplasts) in RBCs. The parasites exist as a ring and/or merozoite forms. A positive sample must show fluorescing rings in at least two RBCs. A negative sample must show no fluorescence within the RBCs.
Stage of Disease
Any Stage of Disease (Early to Late/Chronic Stage)
Limitations
- A single negative FISH test result does not exclude the possibility of Babesia.
- Results should be interpreted in conjunction with other laboratory and clinical findings.
Special Instructions
- In special circumstances, blood smears may be accepted by IGeneX for testing in place of EDTA whole blood. Please contact our Lab Director for more information and authorization. Smears made improperly will not be accepted.
- For Medicare patients, download ABN forms here.
Babesia FISH Results Interpretation >
View Babesia FISH tests >
Babesia PCR Screen (B. microti and/or B. duncani)
The Babesia microti/duncani Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) screen is an assay that detects Babesia DNA in whole blood and speciates to B. microti and B. duncani. The combination of the following three steps imparts a very high specificity and sensitivity to the test:
- Hybridization/Selection
- Amplification of Babesia-specific DNA
- Detection of Babesia-specific amplified DNA fragments
Reference Range
B. microti: Negative, B. microti specific DNA not detected
B. duncani: Negative, B. duncani specific DNA not detected
Clinical Significance
The Babesia microti/duncani PCR screen is an assay that detects Babesia specific DNA (B. microti and/or B. duncani). Babesia ribosomal DNA (rDNA) fragments are hybrid-selected by probes, followed by PCR amplification of selected Babesia rDNA. PCR products are confirmed with Babesia-specific probes in a southern blot assay. The primers and probes used for the selection of Babesia rDNA fragments are designed from published, small ribosomal RNA sequences.
Stage of Disease
Any Stage of Disease (Early to Late/Chronic Stage)
Limitations
- Results should be interpreted in conjunction with other laboratory and clinical findings.
- Test results can only help the physician in confirming a clinical Babesia diagnosis.
Babesia PCR Screen Results Interpretation >
View Babesia PCR tests>
Babesia cePCR - New!
Culture testing is widely considered to be the “gold standard” for diagnosis of Babesia. For many years, Babesia cultures were too expensive and tedious to be practical for laboratory use. Until now. After many years of research and development, IGeneX is pleased to introduce cePCR (Culture-Enhanced PCR) for Babesia.
Download the cePCR datasheet >
Principle
In culturing, a clinical sample from the body (e.g. blood) is incubated in media.
During this incubation period, micro-organisms in the sample grow and multiply. The sample is then tested by PCR to identify the pathogens.
Advantages of Culture-Enhanced PCR
• Provides higher sensitivity than standard PCR testing.
• The only 100% specific method for identification of Babesia.
• Obtaining cultures before antibiotic use improves the chances of identifying the offending microorganism, which improves patient care.
Stage of Disease
Any stage
Complete Test Directory
THE DIRECTORY
GET STARTED TODAY!
The first step in getting tested with IGeneX is to order a collection kit. Choose between a Blood, Urine, or Miscellaneous kit. Doctors can order unlimited quantities of kits at no charge. Patients are required to deposit $20, which is applied to the testing fees.