One of the most difficult parts of treating tick-borne illnesses is diagnosing them in the first place. Lyme disease, for example, often comes with ambiguous symptoms, like fatigue and joint pain, that can lead it to be misdiagnosed.
Although it’s the most well-known, Lyme disease is not the only tick-borne infection to be aware of. Ticks can carry a myriad of illness-causing microorganisms, including those that cause Babesiosis. Having access to a Babesia test makes a huge difference when it comes to the outcome of an infection.

What is Babesia?
Unlike most tick-borne diseases, Babesiosis is caused by microscopic parasites rather than bacteria. Although Babesiosis is usually transmitted by ticks, it can also be transmitted through blood transfusions (FDA), transplants, or from a pregnant parent to their baby.
Babesiosis is also the most common Lyme disease co-infection, which occurs when an organism (in this case, a tick) is infected with more than one infection simultaneously. This is why providers recommend a Babesia test if a patient is also being tested for Lyme.
Babesia grows and reproduces inside the red blood cells of an infected person or animal, much like the malaria parasite. Symptoms of human babesiosis may include:
- Chills
- High fever
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Muscle or joint aches
People with later-stage Babesiosis may experience symptoms like shortness of breath, chest or hip pain, and drenching sweats.
In some cases, Babesia causes no symptoms, while in rare cases, it can be fatal. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC, Babesiosis has a death rate of 0.57%. It has a higher fatality rate amongst the elderly and people who are immunocompromised.
In the United States, Babesiosis is common in the same areas where Lyme disease occurs. This is because it’s transmitted by the same ticks. Cases of Babesiosis have been found in all fifty states, thanks to an increased spread of ticks and people traveling. Babesiosis may even be more common than Lyme disease, although Lyme disease is more widely reported.
Babesia Tests: The Babesia ImmunoBlot
The particular way that Babesia infects and reproduces in red blood cells has implications for diagnostic testing. If you know or suspect you have been bitten by a tick that may carry Babesia, testing is imperative for treatment. That’s where the Babesia ImmunoBlot comes in.
The Babesia ImmunoBlot tests for multiple species of Babesia that can infect humans. When compared with other Babesia tests, what sets this one apart?
IGeneX’s Babesia Immunoblot is unique because it:
- Can detect multiple species of Babesia in one test.
- Detects the full spectrum of the disease, whether someone is in the early, active, or late stage.
- Uses recombinant proteins and not proteins from cultures.
- Is easier to interpret than other tests, and is more sensitive and specific.
- Can detect the most widespread variants in the U.S., Babesia microti and B. duncani.
- Avoids the process of visualizing slides through a microscope
- This is the first test of its kind that is able to detect antibodies. These kinds of tests are known as serologic tests.

The Difference of the Immunoblot is Clear
IGeneX ImmunoBlots are much easier to interpret than other tests used to detect Babesiosis, such as IFA. Also, because they use recombinant antigens and include multiple species, ImmunoBlots are more sensitive and specific.
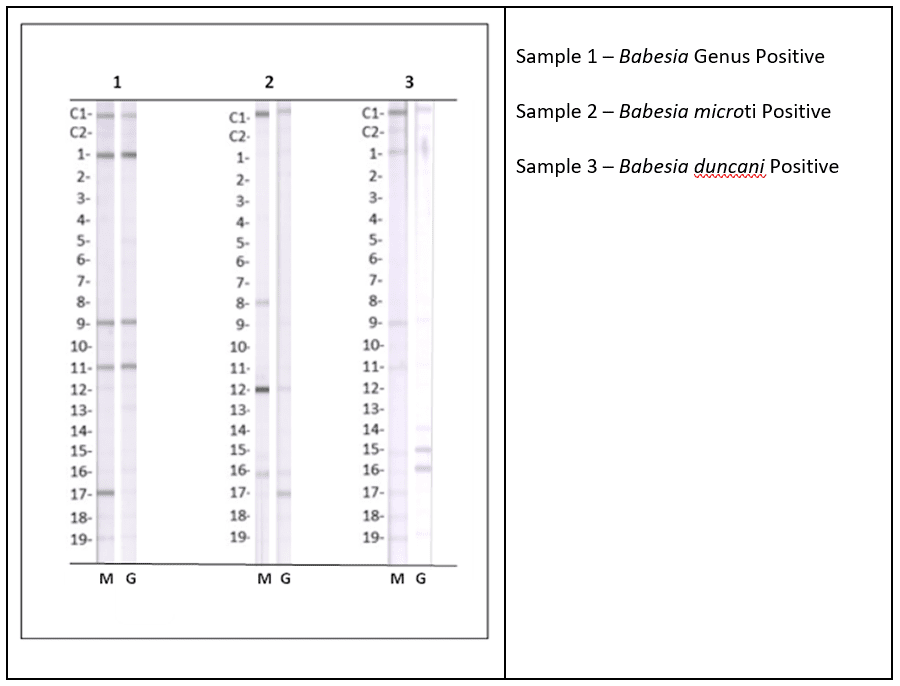
In addition to using ImmunoBlots to test for Babesia, IGeneX recommends using other testing methods, as not all patients produce antibodies and they could be seronegative.
Additional Babesia tests that IGeneX offers include:
- Babesia IFA: Detects antibodies that target Babesia in human serum, and can be used at any stage of the disease. While the ImmunoBlot is a superior test to the IFA, the Babesia IFA is an option for patients in states where the ImmunoBlot is not available, i.e., New York.
- Babesia FISH: The Babesia Fluorescent In-Situ Hybridization is highly specific and uses a blood smear to detect Babesia. This test can be used at any stage of the disease.
- Babesia PCR Screen: Detects Babesia-specific DNA, and is very high in specificity and sensitivity. It can also be used at any stage of the disease.
If a Babesia infection and symptoms are present, your provider will most likely recommend antimicrobial treatment.
Of course, the best way to avoid a tick-borne infection is to try to avoid tick bites in the first place. You can help to minimize your risk by covering arms and legs when you’re in areas where ticks are common, using bug spray with DEET or lemon-eucalyptus oil, and thoroughly checking yourself, your family, and pets, after going into areas that may have ticks.

